SCHOOL OF ALLIED HEALTH SCIENCES
VMRF-DU,SALEM
LET US FIGHT RETINOBLASTOMA
RETINOBLASTOMA AWARENESS WEEK ,MAY 11-MAY 17 2020
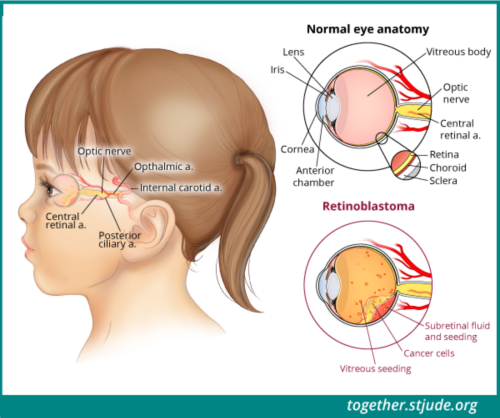
RETINOBLASTOMA
Retinoblastoma is the most common and life-threatening eye cancer in very young children, new born to 3 years of age, generally resulting in removal of the eye. Each year, more than 5000 new cases of retinoblastoma are diagnosed in the World, of which a third (over 1500) are diagnosed in India.

There are two types of Retinoblastoma
Intraocular. This means that cancer occurs in 1 or both eyes, but has not spread into surrounding tissues or other parts of the body.
Extraocular. The cancer has spread to tissues around the eye or to other parts of the body.
Small tumor(s) located only in the retina
No tumor is larger than 3 millimeters (mm)
No tumor is closer than 2 disc diameters (DD) from the fovea (the central “pit” of the retina) or 1 DD from the optic nerve
No vitreous seeding (tumor floating in the eye) or retinal detachment
Tumor(s) located only in the retina
Any location in the retina
No vitreous seeding
No retinal detachment more than 5 mm from tumor base
Fine diffuse (spread throughout) or localized (located in 1 spot) vitreous seeding
Retinal detachment: more than Group B and up to total retinal detachment
No vitreous/sub-retinal “snowballs” or masses
Massive vitreous/sub-retinal seeding
Vitreous or sub-retinal snowballs/masses
Retinal detachment: more than Group B and up to total retinal detachment
No visual potential, or presence of 1 or more:
Tumor in CB/anterior segment
Neovascular glaucoma. This usually results in increased pressure within the eye as a result of blood vessels growing into the anterior segment of the eye and represents an advanced stage of retinoblastoma.
Vitreous hemorrhage, which is bleeding from the eye
Phthisical/prephthisical (deteriorating) eye
Hyphema, which is blood in the anterior of the eye/corneal staining
Orbital cellulitis-like presentation, which means the eye looks similar to the signs of an infection, but there is no infection
Tumor anterior to anterior hyaloids, which means the tumor is behind the thin membrane that separates the vitreous from other parts of the eye. Vitreous is the white gel-like part of the eye.
This staging system applies to cancer that has spread outside of the eye, either to the tissues around the eye or the central nervous system (CNS), bone marrow, or lymph nodes.
Stage 0 (zero):
This means that the cancer is inside the eye and has not spread outside of the eye.
Stage I:
A classification of stage I means that eye has already been removed and there is some microscopic spread to the optic nerve. These patients need adjuvant chemotherapy after surgery.
Stage II:
This stage means that the tumor has spread to the optic nerve or the sclera, which is the white part of the eye. Patients with this stage need adjuvant chemotherapy and possibly radiation therapy.
Stage III:
This means that the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes or the bony cavity that surrounds the eyeball. It is divided into 2 substages, called stage IIIa and stage IIIb, depending on where the tumor has spread. The treatment for this stage involves both chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Stage IV:
In stage IV, the tumor has spread to distant areas of the body outside the eye, via the lymphatic system and blood vessels. Stage IV is divided into substages of IVa and IVb.
Stage IVb is further divided into IVb1, IVb2, and IVb3, depending on the location of the spread. This stage of extraocular retinoblastoma is treated with high-dose chemotherapy followed by stem cell rescue. This means that the child’s stem cell/bone marrow cells are replaced with healthy cells.
Symptoms and Signs
Children with retinoblastoma often experience the following symptoms or signs. Sometimes, children with retinoblastoma do not have any of these changes.
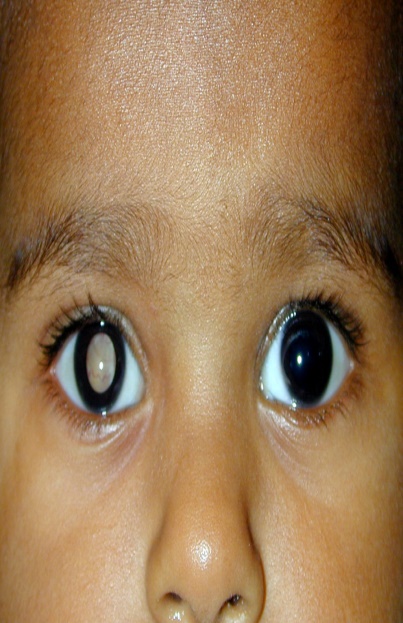
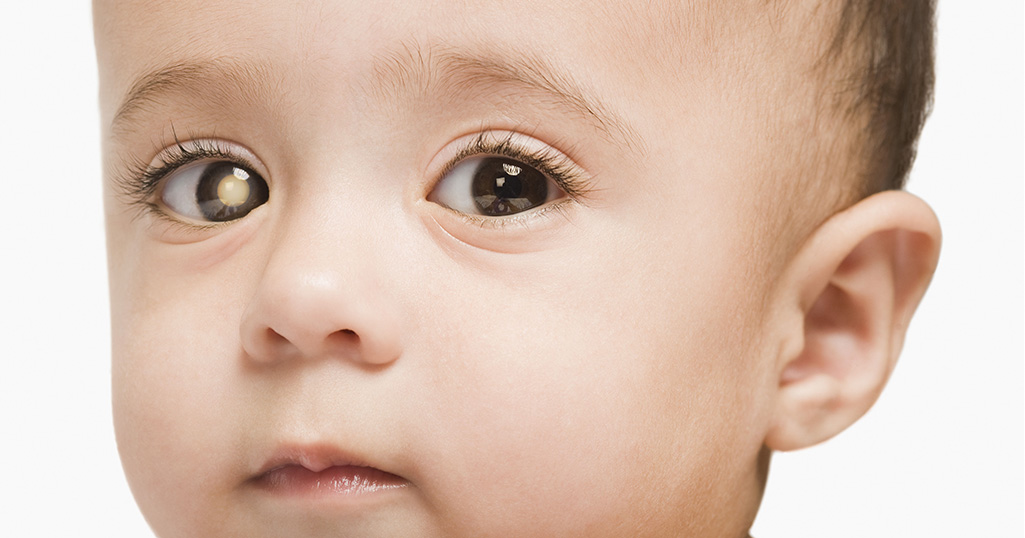
A pupil that looks white or red, instead of the normal black
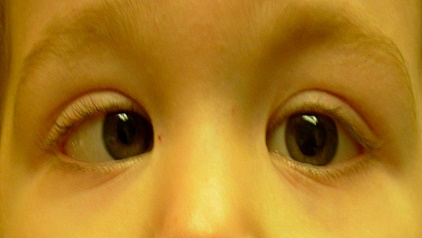
A crossed eye, which is an eye looking either toward the ear or toward the nose

Poor vision
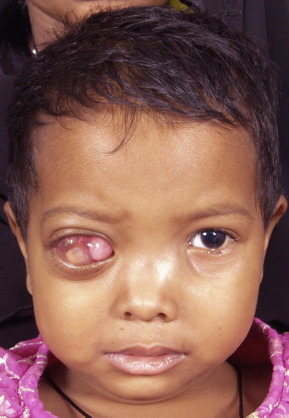
A red, painful-looking eye
An enlarged pupil
Different-colored irises

Diagnostic Tests for Retinoblastoma
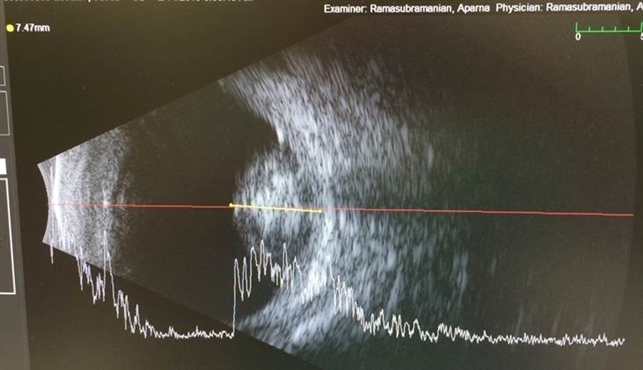
Ultrasound:
An ultrasound uses sound waves to create pictures of the internal organs. A transmitter that emits sound waves is moved over the child’s body. A tumor generates different echoes of the sound waves than normal tissue does, so when the waves are bounced back to a computer and changed into images, based on which a mass inside the body is located. The procedure is painless.
Computed tomography (CT or CAT) scan:
A CT scan takes pictures of the inside of the body using x-rays taken from different angles. A computer combines these images into a detailed, 3-dimensional image that shows any abnormalities or tumors. A CT scan can be used to measure the tumor’s size or find cancer outside of the eye. Sometimes, a special dye called a contrast medium is given before the scan to provide better detail on the image. This dye can be injected into a patient’s vein or given as a pill or liquid to swallow.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI):
An MRI uses magnetic fields, not x-rays, to produce detailed images of the brain and spinal column. MRI can also be used to measure the tumor’s size. A special dye called a contrast medium is given before the scan to create a clearer picture. This dye can be injected into a patient’s vein or given as a pill or liquid to swallow.
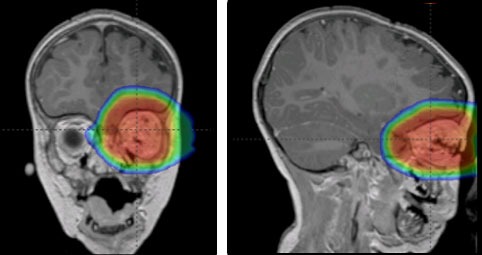
MRI or CT scan of the brain:
These tests may be recommended to find out if there is an abnormality of the pineal gland, which is a small gland in the brain that regulates the body’s response to light. It is recommended that these scans be performed once every 6 months until age 5 for children with the genetic form of retinoblastoma, which includes those with bilateral disease and those with unilateral disease with a family history of the disease. Very young children with a tumor in 1 eye who do not have a family history of the disease may also be at risk, and these tests may be recommended. Scans may also be recommended years after treatment for children who have received external-beam radiation therapy , either as a baseline in case of problems in the future, or to determine the cause of a new symptom or sign of a problem.
Different Types of Treatment
The spread of cancer to different parts can be controlled or stopped by timely diagnosis and management.The treatment plans include and are not limited to
Cryotherapy
Thermotherapy
Chemotherapy
Radiation therapy
High-dose chemotherapy with stem cell rescue
Surgery -Enucleation
ரெட்டினோபிளாஸ்டோமா
விழிப்புணர்வு
வாரம்,
மே 11-மே 17 2020
ரெட்டினோபிளாஸ்டோமா
ரெட்டினோபிளாஸ்டோமா என்பது மிகச் சிறிய குழந்தைகளில் மிகவும் பொதுவான மற்றும் உயிருக்கு ஆபத்தான கண் புற்றுநோயாகும், இந்நோயானது பிறந்த குழந்தை முதல் 3 வயது குழந்தை வரை இதன் தாக்கத்தை ஏற்படுத்தும். இந்த தீவிரமான நோய் கண்களை அகற்றும் அளவிற்கு கொடிய நோய் ஆகும் .ஒவ்வொரு ஆண்டும், உலகில் 5000 க்கும் மேற்பட்ட புதிய ரெட்டினோபிளாஸ்டோமா நோய்கள் கண்டறியப்படுகின்றன, அவற்றில் மூன்றில் ஒரு பங்கு (1500 க்கும் மேற்பட்டவை) இந்தியாவில் கண்டறியப்படுகின்றன.

ரெட்டினோபிளாஸ்டோமாவில் இரண்டு வகைகள் உள்ளன
வகை A:
விழித்திரையில் மட்டுமே அமைந்துள்ள சிறிய கட்டி (கள்)
எந்த கட்டியும் 3 மில்லிமீட்டருக்கு (மிமீ) பெரிதாக இல்லை
எந்தக் கட்டியும் ஃபோவியாவிலிருந்து 2 வட்டு விட்டம் (டி.டி) (விழித்திரையின் மைய “குழி”) அல்லது பார்வை நரம்பிலிருந்து 1 டி.டி.
விட்ரஸ் கட்டி அல்லது விழித்திரைப் பற்றின்மை .
வகை B:
கட்டி (கள்) விழித்திரையில் மட்டுமே அமைந்துள்ளது
விட்ரஸ் கட்டி இருக்காது
கட்டி தளத்திலிருந்து 5 மி.மீ க்கும் அதிகமான விழித்திரைப் பற்றின்மை
வகை C:
புற்றுநோய் முழுவதும் பரவுகிறதுஅல்லது 1 இடத்தில் அமைந்துள்ளது
விட்ரஸ் கட்டி
விழித்திரைப் பற்றின்மை: குழு B ஐ விட அதிகமாக மற்றும் மொத்த விழித்திரைப் பற்றின்மை வரை
விட்ரஸ் / சப்-ரெட்டினல் “பனிப்பந்துகள்” இல்லை
வகை D:
அதிகப்படியான விட்ரஸ் கசிவு / துணை விழித்திரை கசிவு
விட்ரஸ் அல்லது துணை விழித்திரை பனிப்பந்துகள் /
விழித்திரைப் பற்றின்மை: வகை B ஐ விடவும், மொத்த விழித்திரைப் பற்றின்மை வரை
பார்வைத் திறன் இல்லை, அல்லது பின்வருவனவற்றில் ஒன்று அல்லது அதற்கு மேற்பட்டவை:
சுருங்கியகண்
எக்ஸ்ட்ராகுலர் ரெட்டினோபிளாஸ்டோமாவிற்கான சர்வதேச வகைப்பாடு அமைப்பு
கண்ணுக்கு வெளியே பரவியிருக்கும் புற்றுநோய்க்கு, கண்ணைச் சுற்றியுள்ள திசுக்களுக்கு அல்லது மத்திய நரம்பு மண்டலம் (சிஎன்எஸ்), எலும்பு மஜ்ஜை அல்லது நிணநீர் கணுக்களுக்கு இந்த நிலை அமைப்பு பொருந்தும்.
நிலை 0 (பூஜ்ஜியம்):
இதன் பொருள் புற்றுநோயானது கண்ணுக்குள் உள்ளது மற்றும் கண்ணுக்கு வெளியே பரவவில்லை.
நிலை I :
இதன் வகைப்பாடு என்பது கண் ஏற்கனவே அகற்றப்பட்டுவிட்டது மற்றும் பார்வை நரம்புக்கு சில நுண்ணிய பரவல் உள்ளது. இந்த நோயாளிகளுக்கு அறுவை சிகிச்சைக்குப் பிறகு துணை கீமோதெரபி தேவை.
நிலை II:
இந்த நிலை என்பது கண்ணின் வெள்ளைப் பகுதியான பார்வை நரம்பு அல்லது ஸ்க்லெராவுக்கு கட்டி பரவியுள்ளது என்பதாகும். இந்த நிலை நோயாளிகளுக்கு துணை கீமோதெரபி மற்றும் கதிர்வீச்சு சிகிச்சை தேவை.
நிலை III:
இதன் பொருள் புற்றுநோய் நிணநீர் அல்லது கண் பார்வையைச் சுற்றியுள்ள எலும்பு குழிக்கு பரவியுள்ளது. கட்டி எங்கு பரவியது என்பதைப் பொறுத்து இது நிலை IIIa மற்றும் நிலை IIIb என 2 மூலக்கூறுகளாக பிரிக்கப்பட்டுள்ளது. இந்த கட்டத்திற்கான சிகிச்சையானது கீமோதெரபி மற்றும் கதிர்வீச்சு சிகிச்சை இரண்டையும் உள்ளடக்கியது.
நிலை IV:
நிலை IV இல், கட்டி கண்ணுக்கு வெளியே, நிணநீர் மண்டலம் மற்றும் இரத்த நாளங்கள் வழியாக உடலின் தொலைதூர பகுதிகளுக்கு பரவியுள்ளது. நிலை IV a வா மற்றும் நிலை IVb மூலக்கூறுகளாக பிரிக்கப்பட்டுள்ளது.
நிலை IVb மேலும் பரவலின் இருப்பிடத்தைப் பொறுத்து IVb1, IVb2 மற்றும் IVb3 என பிரிக்கப்பட்டுள்ளது. எக்ஸ்ட்ராகுலர் ரெட்டினோபிளாஸ்டோமாவின் இந்த நிலை உயர்-அளவிலான கீமோதெரபி மூலம் சிகிச்சையளிக்கப்படுகிறது, அதைத் தொடர்ந்து ஸ்டெம் செல் மீட்பு. இதன் பொருள் குழந்தையின் ஸ்டெம் செல் / எலும்பு மஜ்ஜை செல்கள் ஆரோக்கியமான செல்கள் மூலம் மாற்றப்படுகின்றன.
அறிகுறிகள்
ரெட்டினோபிளாஸ்டோமா கொண்ட குழந்தைகள் பெரும்பாலும் பின்வரும் அறிகுறிகள் அல்லது அறிகுறிகளை அனுபவிக்கின்றனர்.
கண் பாவை (Pupil)வெள்ளை அல்லது சிவப்பு நிறமாக இருக்கும்

மாறுகண் இருக்கலாம்

கண் பார்வை குறைபாடு இருக்கலாம்
கண் சிவத்தல் மற்றும் வலி ஏற்படுதல்

• விரிவாக்கப்பட்ட கண் பாவை (Pupil)

• வெவ்வேறு வண்ண கருவிழிகள்

ரெட்டினோபிளாஸ்டோமாவிற்கான நோயறிதல் சோதனைகள்
• அல்ட்ராசவுண்ட்:
அல்ட்ராசவுண்ட் உள் உறுப்புகளின் படங்களை உருவாக்க ஒலி அலைகளைப் பயன்படுத்துகிறது. ஒலி அலைகளை வெளியிடும் ஒரு டிரான்ஸ்மிட்டர் குழந்தையின் உடலுக்கு மேல் நகர்த்தப்படுகிறது. ஒரு கட்டி சாதாரண திசுக்களை விட ஒலி அலைகளின் வெவ்வேறு எதிரொலிகளை உருவாக்குகிறது, எனவே அலைகள் மீண்டும் ஒரு கணினியில் குதித்து படங்களாக மாற்றப்படும்போது, அதன் அடிப்படையில் உடலுக்குள் ஒரு அதிகப்படியாக அமைந்திருக்கும் உருவங்களை பதிவு செய்யும். உருவங்களை பதிவு செய்யும் இந்த செயல்முறை வலியற்றது.

• கம்ப்யூட்டட் டோமோகிராபி (CT SCAN) ஸ்கேன்:
ஒரு சி.டி ஸ்கேன் வெவ்வேறு கோணங்களில் இருந்து எடுக்கப்பட்ட எக்ஸ்-கதிர்களைப் பயன்படுத்தி உடலின் உட்புறத்தின் படங்களை எடுக்கும். ஒரு கணினி இந்த படங்களை ஒரு விரிவான, 3 பரிமாண படமாக இணைக்கிறது, இது ஏதேனும் அசாதாரணங்கள் அல்லது கட்டிகளைக் காட்டுகிறது. கட்டியின் அளவை அளவிட அல்லது கண்ணுக்கு வெளியே இருக்கும் புற்றுநோயைக் கண்டுபிடிக்க CT ஸ்கேன் பயன்படுத்தப்படலாம். சில நேரங்களில், படத்தைப் பற்றி சிறந்த விவரங்களை வழங்க ஸ்கேன் செய்வதற்கு முன்பு கான்ட்ராஸ்ட் மீடியம் எனப்படும் சிறப்பு சாயம் வழங்கப்படுகிறது. இந்த சாயத்தை நோயாளியின் நரம்புக்குள் செலுத்தலாம் அல்லது விழுங்குவதற்கு ஒரு மாத்திரை அல்லது திரவமாக கொடுக்கலாம்.
• காந்த அதிர்வு இமேஜிங் (MRI)
ஒரு எம்.ஆர்.ஐ மூளை மற்றும் முதுகெலும்பு நெடுவரிசையின் விரிவான படங்களை உருவாக்க எக்ஸ்-கதிர்கள் அல்ல, காந்தப்புலங்களைப் பயன்படுத்துகிறது. கட்டியின் அளவை அளவிட எம்ஆர்ஐ பயன்படுத்தப்படலாம். தெளிவான படத்தை உருவாக்க ஸ்கேன் செய்வதற்கு முன்பு கான்ட்ராஸ்ட் மீடியம் என்று அழைக்கப்படும் ஒரு சிறப்பு சாயம் வழங்கப்படுகிறது. இந்த சாயத்தை நோயாளியின் நரம்புக்குள் செலுத்தலாம் அல்லது விழுங்குவதற்கு ஒரு மாத்திரை அல்லது திரவமாக கொடுக்கலாம்.

.
• மூளையின் MRIஅல்லது சCT ஸ்கேன்:
பினியல் சுரப்பியின் அசாதாரணத்தன்மை உள்ளதா என்பதைக் கண்டறிய இந்த சோதனைகள் பரிந்துரைக்கப்படலாம், இது மூளையில் ஒரு சிறிய சுரப்பி ஆகும், இது ஒளியின் உடலின் பதிலைக் கட்டுப்படுத்துகிறது. ரெட்டினோபிளாஸ்டோமாவின் மரபணு வடிவத்தில் உள்ள குழந்தைகளுக்கு 5 வயது வரை ஒவ்வொரு 6 மாதங்களுக்கும் ஒரு முறை இந்த ஸ்கேன்கள் செய்ய பரிந்துரைக்கப்படுகிறது, இதில் இருதரப்பு நோய் உள்ளவர்கள் மற்றும் நோயின் குடும்ப வரலாற்றைக் கொண்ட ஒருதலைப்பட்ச நோய் உள்ளவர்கள் உள்ளனர். நோயின் குடும்ப வரலாறு இல்லாத 1 கண்ணில் கட்டி உள்ள மிகச் சிறிய குழந்தைகளும் ஆபத்தில் இருக்கக்கூடும், மேலும் இந்த சோதனைகள் பரிந்துரைக்கப்படலாம். வெளிப்புற-பீம் கதிர்வீச்சு சிகிச்சையைப் பெற்ற குழந்தைகளுக்கு சிகிச்சையளிக்கப்பட்ட பல ஆண்டுகளுக்குப் பிறகு ஸ்கேன் பரிந்துரைக்கப்படலாம், எதிர்காலத்தில் பிரச்சினைகள் ஏற்பட்டால் அல்லது ஒரு புதிய அறிகுறி அல்லது பிரச்சினையின் அறிகுறியின் காரணத்தை தீர்மானிக்க.
சிகிச்சையின் வெவ்வேறு வகைகள்
பல்வேறு பகுதிகளுக்கு புற்றுநோய் பரவுவதை சரியான நேரத்தில் கண்டறிதல் மற்றும் நிர்வாகத்தால் கட்டுப்படுத்தலாம் அல்லது நிறுத்தலாம்.
கிரையோதெரபி
தெர்மோதெரபி
கீமோதெரபி
கதிர்வீச்சு சிகிச்சை

ஸ்டெம் செல் மீட்புடன் உயர்-அளவிலான கீமோதெரபி
அறுவை சிகிச்சை (கண்களின் அணுக்கருவை நீக்குதல்)

ரெட்டினோபிளாஸ்டோமா பற்றிய விழிப்புணர்வை ஏற்படுத்துவோம்!!!